Bladder most cancers is at present handled in its earlier levels by localized intravesical chemotherapy or immunotherapy after eradicating the tumor. Nonetheless, recurrences happen in as much as 70% of sufferers at 5 years, whereas as much as 30% fail to reply. This implies a relentless want to watch and retreat these sufferers, driving prices sky-high for the remedy of this type of most cancers. A brand new examine in Nature Nanotechnology explores the potential use of nanobots to reinforce the therapeutic efficacy of intravesical remedy of bladder most cancers.
 Examine: Urease-powered nanobots for radionuclide bladder most cancers remedy
Examine: Urease-powered nanobots for radionuclide bladder most cancers remedy
At current, for bladder cancers that haven’t reached the stage of muscle invasion, the tumor is eliminated, adopted by the intravesical use of the immunotherapeutic agent Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus Calmette–Guérin (BCG) or the chemotherapeutic drug mitomycin C, singly or together. Points with this mode of remedy embrace non-uniform dispersion all through the bladder, fast transit, and low adhesion of the agent to focus on tissue, resulting in sedimentation throughout the bladder. All these are associated to the fixed arrival of contemporary urine into the bladder.
The best agent ought to be capable to enter tumor tissue to sufficient depths, deal with the entire tumor, and be appropriate with human tissue. Nanobots are self-propelled nanoparticles that could be of immense utility in intravesical chemotherapy as a result of they will diffuse and blend a lot better in physique fluids like urine in comparison with standard drug formulations or odd nanoparticles.
Within the present examine, the main focus is on the power of nanobots to enhance the low therapeutic efficacy of intravesical bladder most cancers remedy. The researchers used radiolabelled nanobots of 450 nm diameter constructed on a mesoporous silica base.
These have been designed to propel themselves utilizing chemical power from reactions based mostly on substrates within the surrounding fluid. On this case, urea break up by the enzyme urease, carried on the nanobots.
The manufacturing of ammonia and CO2 across the particle throughout the response enhanced the movement of those particles. Specifically, this drives a swarming habits that’s related to increased convection and mixing and inhibition of sedimentation. This provides them immense potential as carriers for radionuclide remedy (RNT).
They have been examined for therapeutic efficacy in bladder most cancers in a mouse mannequin.
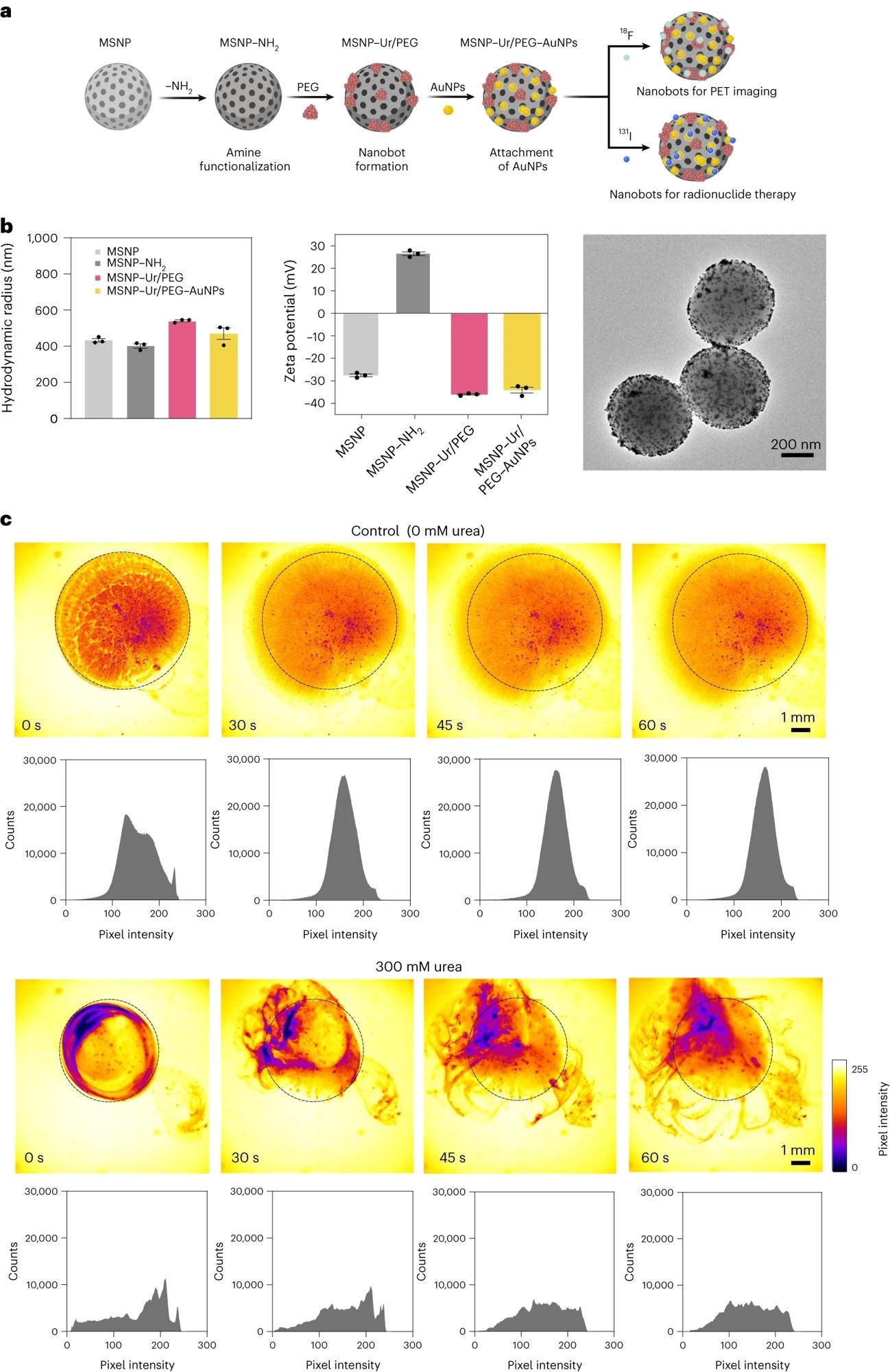
a, Schematic illustration of the nanobot fabrication course of and radiolabelling. Ur, urease. b, Left: nanobot characterization by dynamic mild scattering (n = 3, technical replicates). Knowledge are offered as imply values and error bars symbolize the s.e.m. Centre: zeta potential (n = 3, technical replicates) Knowledge are offered as imply values and error bars symbolize the s.e.m. Proper: transmission electron microscopy picture. c, Snapshots depicting the nanobot movement dynamics within the absence and presence (300 mM) of urea as gas, and corresponding pixel depth histograms for the ROI marked by a circle. Panel a created with BioRender.com.
What did the examine present?
Each ex vivo and in vivo experiments confirmed that nanobots achieved the next focus on the tumor website, at 8-fold elevated ranges confirmed by positron emission tomography (PET). The presence of urea led to lively dispersion of the particles with swarming coordinated movement.
Efficient nanobot movement occurred solely within the presence of urease and urea, and with out enzymatic exercise, tumor uptake of the labeled nanobots didn’t happen.
Affirmation of exercise was first sought utilizing optimized optical distinction strategies based mostly on polarization-dependent scattered light-sheet microscopy. This confirmed that the tumors had been penetrated by the nanobots in ex vivo experiments. Conversely, little adherence or penetration occurred in wholesome bladder tissue.
This methodology was additionally validated for in vivo observations of nanobots, because it gives high-grain decision in a 3D format.
Not like water, the urea-containing surroundings led to the profitable self-propulsion of the nanobots to build up throughout the tumor tissue. This can be partly as a result of the diseased bladder epithelium is extra permeable to those particles by the breakdown of epithelial tight junctions. Additionally, the nanobots themselves could assault the tumor’s extracellular matrix (ECM) due to the essential ammonia produced by the urease-catalyzed response.
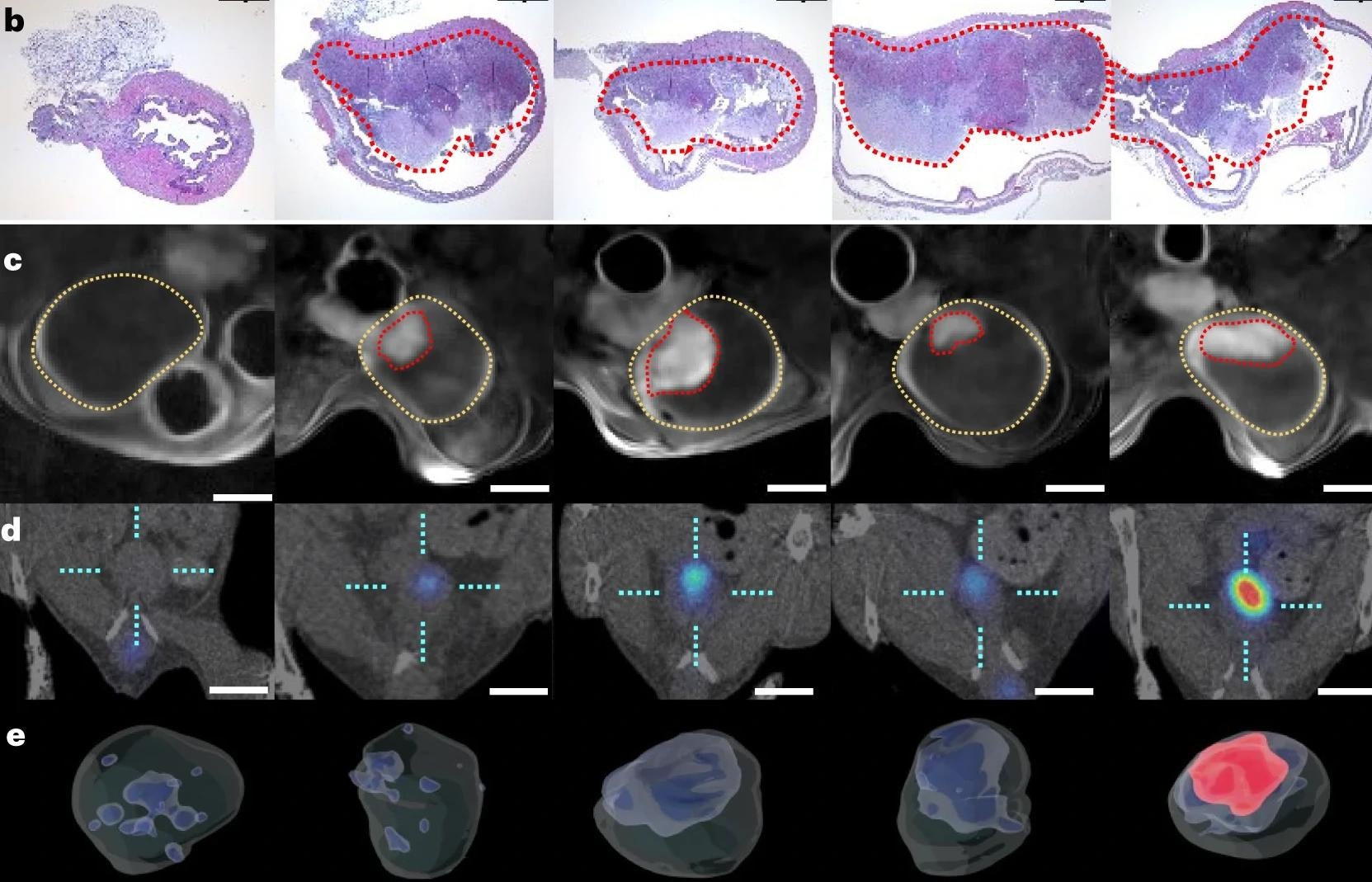
With the mouse mannequin, when the mice have been handled with nanobots carrying radioiodine for RNT instilled into the bladder, the tumors shrank by about 90%, even at low doses. Radioiodine is extensively utilized in RNT, being a beta-particle emitter with an 8-day half-life and able to penetrating to a depth of 0.8 mm (about 0.03 in) into tissue.
This means that the lively motion of the nanobots enhances tumor accumulation. This favors their scientific translation. Even at increased doses, the animals remained inside normal weight limits, with an excellent larger fall in tumor quantity.
“This means that 131I-carrying nanobots can successfully deal with bladder tumors in confined areas, presenting another remedy for situations the place conventional therapeutic approaches, comparable to BCG, routinely fail.”
What are the implications?
The outcomes counsel urease-powered nanobots may very well be “environment friendly supply nanosystems for bladder most cancers remedy.”
Supply hyperlink