 Nothing ruins a wonderfully good runner like plantar fasciitis, the dreaded snake chunk of the heel and arch of the foot. In essence, it’s nasty foot ache — notably heel ache — that stops us from working. As soon as it units in, is likely one of the most menacing and cussed situations.
Nothing ruins a wonderfully good runner like plantar fasciitis, the dreaded snake chunk of the heel and arch of the foot. In essence, it’s nasty foot ache — notably heel ache — that stops us from working. As soon as it units in, is likely one of the most menacing and cussed situations.
Ultrarunners appear notably vulnerable to heel and arch ache. Each uphill and downhill working stresses the foot: the ups stressing the tender tissues of the plantar arch, and the downhills offering ample pounding for the joints.
It’s okay to name your foot and heel ache plantar fasciitis — similar to that Coke on the help station that is likely to be Pepsi or RC Cola. However make sure that you — and your physician, PT, chiropractor, LMT or different healthcare helpers — are conscious of all of the totally different sources of foot ache. Consciousness is step one in complete remedy and quick restoration from the dreaded “PF” and its brethren.
Plantar Fasciitis, Outlined
The plantar fascia is the thick connective tissue that runs from the bottom of the heel, to the bones of the forefoot. Collectively, with intrinsic foot and ankle muscular tissues, it helps the arch of the foot and helps switch power from the forefoot to the rearfoot and ankle, and up the leg.
By definition, in a really literal sense, fasciitis is an energetic irritation of that tissue.
However is foot and heel ache at all times plantar fasciitis? In a scientific sense, one can solely have fasciitis if an energetic inflammatory occasion is going on. Since irritation solely lasts 20 days, certainly, not everybody with persistent foot ache actually has fasciitis.
Not all tissue paper is Kleenex. Not all lip balm is Chapstick. And so it goes, not all heel and arch ache is plantar fasciitis. However as Shakespeare as soon as mentioned, “Is foot ache by every other title, any much less excruciating?”
Nonetheless, to label all foot ache as plantar fasciitis probably limits one’s potential to rapidly and successfully get well from it. Under are another, equally frequent causes of foot ache.
Foot Ache: Differential Prognosis
There are a many potential sources of persistent heel ache and arch ache. Listed here are the most typical I see, clinically:
Gentle tissue sprains and strains. There are a number of main muscular tissues, tendons, and ligaments that span from the heel and ankle to the toes. Moreover the plantar fascia, there are a number of flexor tendons — of muscular tissues originating on the decrease leg — that course their means into the foot.
Any variety of these tissues can turn out to be strained underneath the load of highway and path working. A evaluation of the Guidelines of Tissue Loading explains how a plantar floor tissue can turn out to be irritated.
Nonetheless, since tender tissue tends to heal rapidly given correct remedy, these causes are likely to heal quickly. These with persistent heel ache and arch ache — who see me and different medical of us after weeks, months, and even years of ache — are likely to have a ache generator of various origins:
Joint Ache. There are over two dozen joints within the foot and ankle advanced. With the intense stress of extremely path working, these joints may turn out to be stiff, irritated, or each.
Joints — articulating surfaces of two bones — require however two issues to be blissful:
- Full vary of movement
- Symmetrical, equal loading of surfaces
Appears easy, however working long and hard on uneven surfaces can strip a joint of these two issues.
Vary of movement loss. Joints get the majority of their vitamin from vary of movement. The overwhelming majority of joints within the physique are synovial: two bones surrounded by a leathery capsule stuffed with fluid. The cartilage surfaces obtain little or no blood movement.
With a purpose to obtain vitamin, the joint should “lubricate” itself with the fluid of the joint, absorbing vitamins from the fluid alongside its floor — through common, full vary of movement.
When joints cease shifting by way of their full vary, components of cartilage don’t get this vitamin. The cartilage dries up. And it’s changed with bone. This, by definition is osteoarthritis. Previous that, is ache.
Asymmetrical loading. Joints have the power to maneuver — typically small quantities in a single airplane; typically substantial quantities in lots of instructions. However when working, joint surfaces are designed to be loaded in order that your entire floor of 1 bone impacts flush towards the opposite. This promotes most stability; it additionally ensures that cartilage receives a gradual dose of hydration and vitamins.
Asymmetrical loading happens as the results of irregular working surfaces — uneven, rocky trails, or a cambered/slanted highway–or with inefficient working mechanics.
And when a joint turns into sad, it causes ache. Usually, a painful joint will harm at its exact level of irritation. However joints of the ankle and foot will incessantly refer ache to adjoining areas, out the perimeters or beneath the purpose of irritation, at instances mimicking tender tissue ache.
How will you inform in case you have a tender tissue or joint subject? Under are some comparisons:
Gentle Tissue Ache Traits
- Succinct, reproducible, palpable tissue ache. Can you discover the one spot that’s tender?
- Ache with energetic use: while you do a toe curl or use the muscle (absent weight-bearing), does it harm?
- Ache with passive stretch: is ache produced while you bend again your foot and toes? (once more, with out weight bearing)
- Ache with resisted testing: when flexing your foot and toes, is there ache?
Joint Ache Traits
- Boring, diffuse ache: no discernible “tender spot.” Somewhat, it hops round and you may’t put your finger on it.
- Ache with weight-bearing by way of the joint.
- Ache is worst within the morning, after extended weight-bearing, or after resting, then bearing weight by way of the joint.
- Non-weight-bearing testing — actively flexing and passively stretching the foot — is pain-free.
In case your signs align with the joint ache traits — and in case your foot ache fails to reply to tender tissue plantar fascial remedy approaches — you seemingly have joint ache.
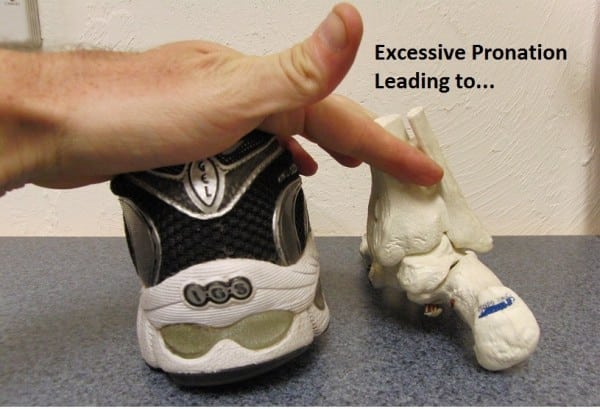
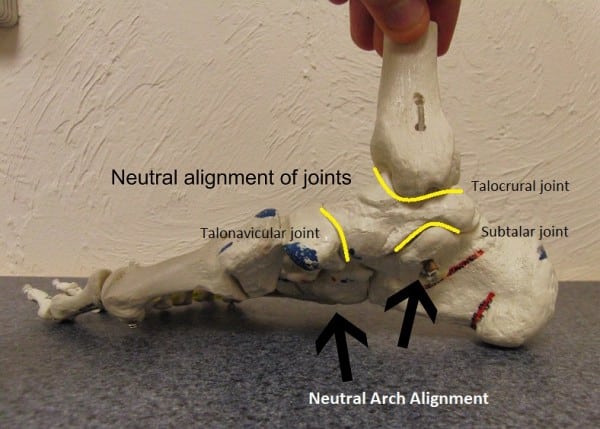
The three regular joint suspects — the talocrural, the subtalar, and the talonavicular — can all turn out to be painful and mimic plantar fascial ache. Every joint lies on the medial plantar floor of the foot, and every is vulnerable to stiffness and asymmetrical loading throughout working.
Above reveals a medial view of the foot, displaying three principal joints of the foot. The talus performs a job in all three: it’s the go-between from the foot and leg bones.
From above, it types the talocrural joint. The principle movement for this joint is “up and down” — it permits the toe-up/toe-down motion that happens within the run stride.
This joint is prime to get stiff, particularly with repetitive downhill working: slightly than easily sliding and gliding, onerous downhill path working may cause jamming forces of the talus into the tibia and fibula. And when this joint will get stiff, it might refer ache in any route across the talus — entrance or again of the ankle (mimicking each anterior tibialis tendonitis and Achilles tendonitis, respectively), or it might spit ache out the facet — particularly the medial ankle and arch.
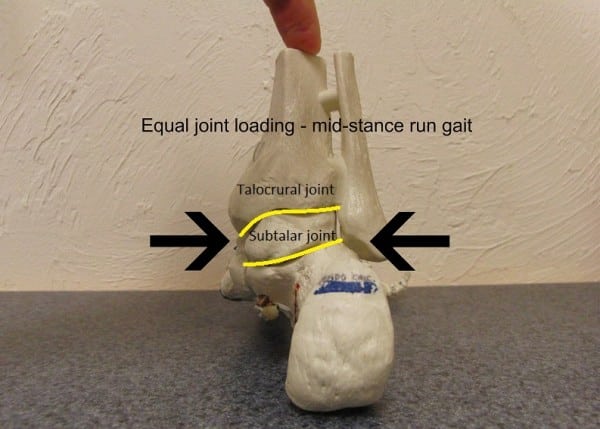
Between the talus and the calcaneus — or heel bone — is the subtalar joint. It’s designed to maneuver in a number of axes, however its main axis of movement is medial to lateral. This joint is of little consequence to the wholesome, regular runner: minor motions happen relying on the gait cycle.
Nonetheless, deviations or inefficiencies — particularly within the foot strike sample — may cause vital ache emanating from the subtalar joint. Extreme lateral foot strike may cause annoying joint compression to the medial side of the joint — mimicking plantar fascial ache!
Lastly is the talonavicular joint. This joint is the first conduit from the fore and midfoot to the ankle and leg. The navicular bone is the “keystone” of the arch. Stiffness or irritation right here can even trigger vital arch ache.
The next are some illustrations of how mechanical forces may cause joint and tender tissue ache:
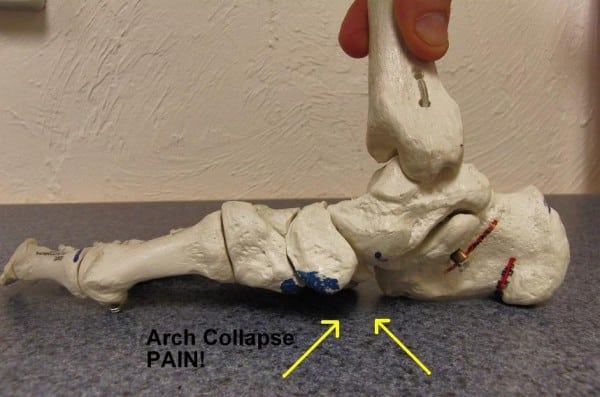
Extreme medial foot touchdown results in over-stressing of the medial arch, or “arch collapse.” This stresses all tissues of the plantar floor and is the first etiology of true plantar fascial ache.
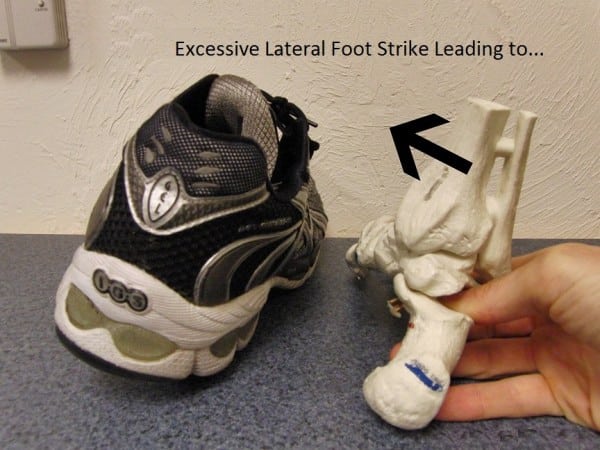
Equally frequent, particularly for quicker path runners, is extreme lateral foot strike:
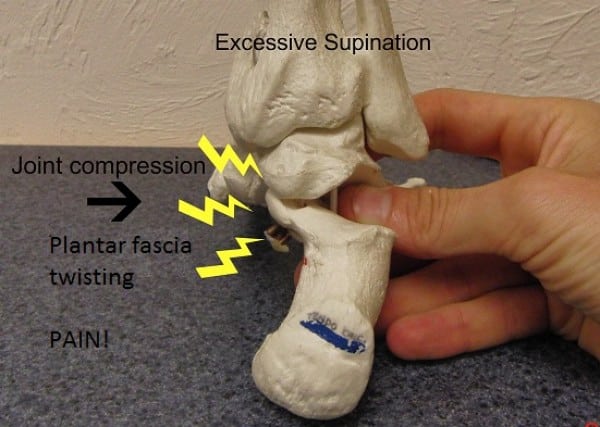
Extreme lateral putting considerably compresses the medial joint floor of the subtalar joint. This compression accounts for a big proportion of non-plantar fascial foot ache circumstances. It refers ache at its web site, but additionally farther down into the arch and alongside the heel bone.
An excessive amount of lateral strike can even trigger plantar fascial torquing: the heel rotating to the proper (within the above image), however the forefoot rotates to the left because it contacts the bottom — including a twisting pressure to the fascia.
Nerve ache. Maybe essentially the most unrecognized and neglected think about heel and foot ache is nerve ache. The peripheral nerves of the ankle and foot originate within the mind, course by way of the backbone, exit the low again and pelvis, and should course — fluidly — by way of the tender tissues of your entire leg.
Repetitive influence forces from working — typically mixed with compromised backbone posture from working all day (or, in our regular lives, sitting) — may cause these nerves to develop “hitches.” This can be a idea referred to as nerve stress.
Nerve stress accumulates within the backbone and legs with age, damage historical past, and working quantity. When nerves lose mobility, they start to create ache — typically similar to tender tissue or joint ache, together with plantar foot ache.
And since the identical repetitive or extreme influence forces that create joint and tender tissue ache additionally create nerve stress, it is extremely frequent for a runner to current with each joint/tender tissue and nerve ache overlay on the identical time.
Virtually each runner (and most people) has some extent of nerve stress. Right here’s a check:
Sit along with your again towards a chair, head and shoulders upright. Prolong your knees straight, with toes up. Word the diploma of “stretch” behind your legs. Then, hunch your head and shoulders. Any enhance in stretch sensation is nerve stress from tensing the nerve on the head and neck.
Nerve Ache Traits
- Ache at relaxation — the hallmark signal of nerve ache overlay: do you’ve any signs in your foot when at relaxation, particularly sitting (particularly, with extended sitting, lengthy after you’ve stood on it)?
- Signs described as burning, buzzing, or uninteresting aching.
- Different signs larger up the leg, particularly: lumbar, buttock, posterior thigh, calf, or shin ache.
Fairly often, a runner who applies tender tissue or joint remedy ideas will get partially higher, however fail to totally get well as a result of they fail to handle the nerve stress element.
Runners and clinicians, alike, want to acknowledge the existence of nerve stress and deal with it concurrent with any tender tissue or joint irritation.
Remedy Approaches
Please talk about any of the next remedy approaches along with your physician, bodily therapist, or chiropractor earlier than performing.
Gentle tissue
These are simple as a result of everybody who [thinks they have] PF does them:
- Relaxation, ice, tender tissue mobilization, stretch, strengthen.
Actual, precise tender tissue plantar ache will heal quickly, given appropriate doses of the remedies above. Those that don’t reply to that method seemingly have a joint or nerve subject.
Joint ache
The 2 remedy approaches to joint ache within the foot embrace full restoration of joint vary of movement and symmetrical loading.
Vary of movement restoration
Ankle dorsiflexion. Regular ankle dorsiflexion is about 20-30 levels past a 90-degree bend on the ankle. When you can’t stretch this far — or in case you have signs in entrance, or wherever across the ankle joint — your signs is likely to be resulting from stiffness there. To mobilize a stiff talocrural joint, strive the next:
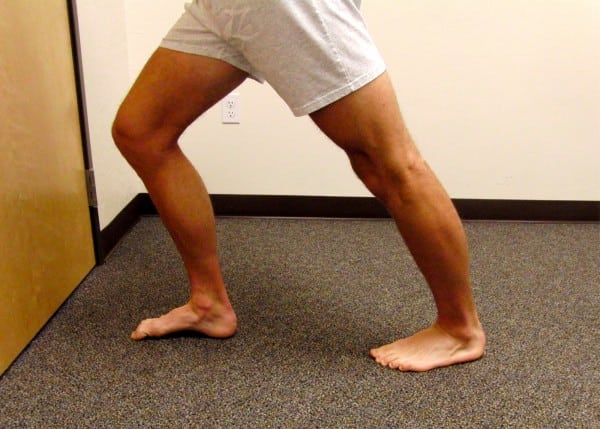
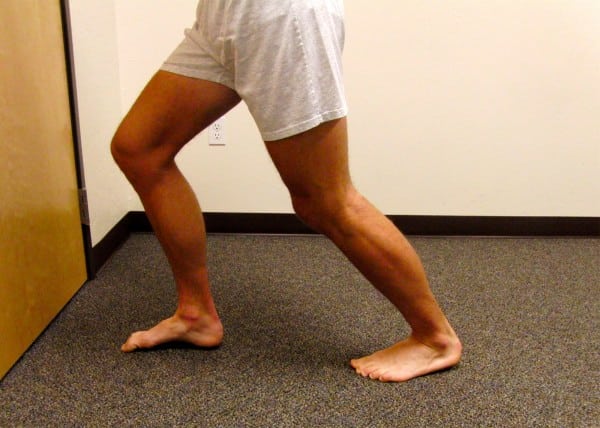
Carry out an ordinary calf stretch, with a couple of minor changes: ensure your stretch foot is completely straight forward. Hold the foot flat, lean ahead with a straight knee till full stress.
Then, slowly bend the knee as a lot as potential with out permitting the heel to rise. Slowly oscillate between a bent and straight knee. This mobilizes the tibia and fibula over the talus, restoring movement to this joint.
Subtalar inversion and eversion. A traditional heel bone ought to be capable of “wiggle” about 10-20 levels facet to facet. To self-test, cross your ankle over the alternative knee. Greedy maintain of your ankle with one hand, drive firmly downward along with your reverse hand on the within of your heel bone.
Can you progress it, in any respect? If not, and you’ve got heel and arch ache on the underside/medial facet of your foot, your signs could also be coming from a stiff subtalar joint.
To self-mobilize, carry out the maneuver described above with agency, gradual, on-and-off downward strain. The diploma of movement might be slight, however the potential for ache aid is substantial when movement is restored right here.
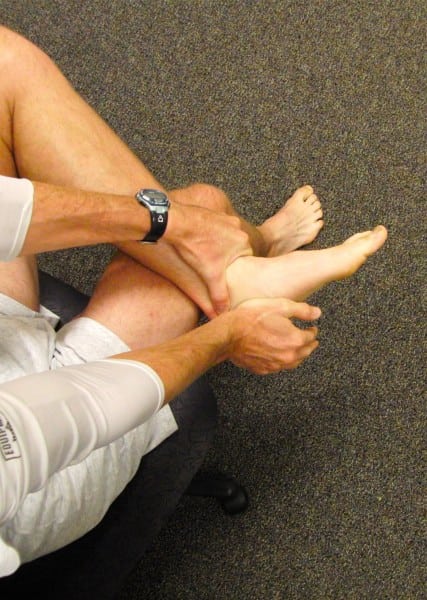
The creator making use of a straight downward strain to the heel bone, stabilizing on the ankle. A traditional heel will “wiggle” a couple of millimeters in each up and down instructions.
Midfoot arch. A traditional midfoot could have some extent of give, each to the arms and when standing on it. In standing, a usually cell foot ought to “sink” a couple of millimeters to the ground.
Shoe orthotics are meant for individuals who are hypermobile of their arch: their arch joints are excessively versatile, and the arch “collapses” (usually outlined as one centimeter or extra) in weight bearing.
Nonetheless, far most of the time, runners have hypomobile arches — they merely don’t transfer sufficient. These of us usually reply poorly to orthotics (typically with no enchancment, and typically they worsen ache).
A hypomobile, stiff arch will profit from self-mobilization. When you’ve got signs that originate farther down the foot, close to the apex of the arch — and your foot lacks any give in standing — strive the next mobilization:
Stand with the stiff foot down. Place your reverse heel instantly on high of the stiffest space — usually the navicular bone, which lies instantly in entrance of the tibia-fibula advanced. Gently, then progressively bear down with substantial weight onto the navicular.
This may increasingly appear scary — check it first. A stiff navicular will give little or no, even with full strain. Ache often comes from pores and skin compression. “Stomp” on and off 10-20 instances. Carry out earlier than and after working, and/or within the morning, when stiff joints are usually stiffest.
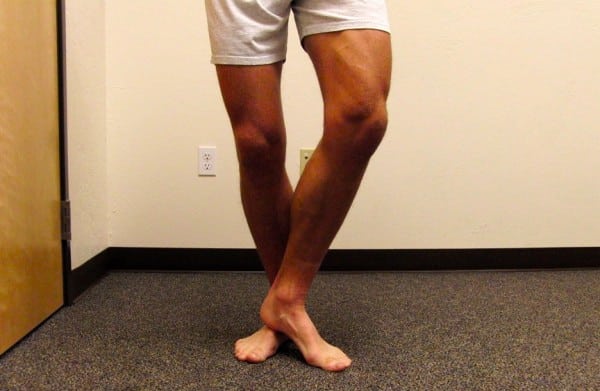
The creator, performing a mid-foot self-mobilization in standing. Strive with soft-heeled footwear on, if too sore with direct pores and skin contact.
Joint Loading Elements
Loading the joint equally is significant to joint happiness. Orthotics could be useful for these with hypermobile ft, as they will stop arch collapse. They’re additionally useful for slower runners with shorter stride lengths. A brief stride tends to incorporate extreme vertical forces (up and down movement).
This vertical loading bears down on the medial arch — past the aptitude of muscular tissues, tendons, and the plantar fascia to assist it. An orthotic can help in sustaining the arch. However in the end, an environment friendly stride that emphasizes regular hip mobility with larger ahead momentum is most essential in stopping arch collapse.
Different essential elements for symmetrical, low-stress loading embrace the place and angle of foot strike. The foot ought to at all times land as near instantly beneath one’s heart of mass as potential. A foot that strikes in entrance, tends to strike:
- On the heel;
- On the surface fringe of the foot (heel or midfoot); or
- On the mid or forefoot, laterally-biased.
A heel strike creates appreciable stiffness by way of the talocrural and subtalar joints. A lateral strike would possibly trigger asymmetrical loading of the subtalar joint, and/or a twisting, torquing pressure by way of the midfoot and plantar fascia (see photograph above). A midfoot or forefoot strike — considerably forward of the physique — will stress out these joints or pressure the plantar fascia.
The most straightforward, sustainable, and essential approach to appropriate a foot strike subject is addressing it proximally with:
- Correct ahead trunk engagement, and
- Shifting the hips such that the foot is “pulled” beneath the physique
After guaranteeing correct foot placement beneath the trunk, shoot for a whole-foot strike, the place all components of the foot are absorbing and sharing influence forces.
Nerve Ache Remedy
To deal with nerve stress, seek advice from the check above, besides make one slight adjustment:
Sit in a chair, slumped ahead. Slowly lengthen the affected leg with toes up. Because the foot and decrease leg rise, slowly lengthen your head on the identical velocity. The diploma of stretch ought to be considerably much less, however nonetheless current.
Maintain one second, then slowly decrease. That is known as a “nerve floss” train: the pinnacle provides the nerve slack that’s taken by the foot, and vice versa. Repeat 10 to twenty instances, and carry out three to 4 instances a day, particularly earlier than and after working. Right here is a video hyperlink for the train.
Name for Feedback (From Bryon)
- Have you ever suffered from heel ache, plantar fasciitis, or different foot ache?
- How did you heal your plantar fasciitis, heel ache, or different foot ache?










I loved even more than you will get done right here. The picture is nice, and your writing is stylish, but you seem to be rushing through it, and I think you should give it again soon. I’ll probably do that again and again if you protect this hike.