A latest research printed within the journal PNAS examines the impression of local weather change on air high quality alerts in america and explores the methods of particular person adaptation to air air pollution.
 Research: Well being and fairness implications of particular person adaptation to air air pollution in a altering local weather. Picture Credit score: James Andrews1 / Shutterstock
Research: Well being and fairness implications of particular person adaptation to air air pollution in a altering local weather. Picture Credit score: James Andrews1 / Shutterstock
Background
Air air pollution is likely one of the main causes of extreme well being issues and untimely dying worldwide. In america, air air pollution has extra detrimental results on weak populations, together with racialized folks and socioeconomically disadvantaged folks.
On days with poor air high quality, the US well being authorities situation alerts advising folks to remain indoors and restrict outside air publicity for cover. Round 15 – 20% of Individuals at the moment defend themselves from poor air high quality by limiting their outside actions.
Latest adjustments in local weather situations have considerably affected air high quality globally. Poor air high quality not solely negatively impacts human well being but in addition will increase healthcare prices. Local weather coverage can provide important and equity-improving well being advantages by bettering air high quality. Growing adaptation to poor air high quality can even forestall well being issues.
On this research, scientists have explored the impression of local weather change on the speed of air high quality alerts within the US over this century. They’ve additionally examined which populations are most affected by poor air high quality and the way local weather insurance policies can enhance adaptation to cut back well being dangers.
Essential observations
The research discovered that the speed of air high quality alerts can improve by 4-fold on common by 2100 if the emission of greenhouse gases and air pollution (particulate matter) shouldn’t be decreased. Air high quality alerts might improve by one month per 12 months by 2100 within the jap United States, representing the areas with excessive Black populations and poorly-housed populations.
As talked about by the scientists, such unequal will increase in air high quality alerts in these low-income areas can adversely have an effect on the difference capability of weak populations to poor air high quality. Poorly structured homes could make the difference much less efficient and even dangerous by letting polluted air infiltrate the homes and cut back indoor air high quality.
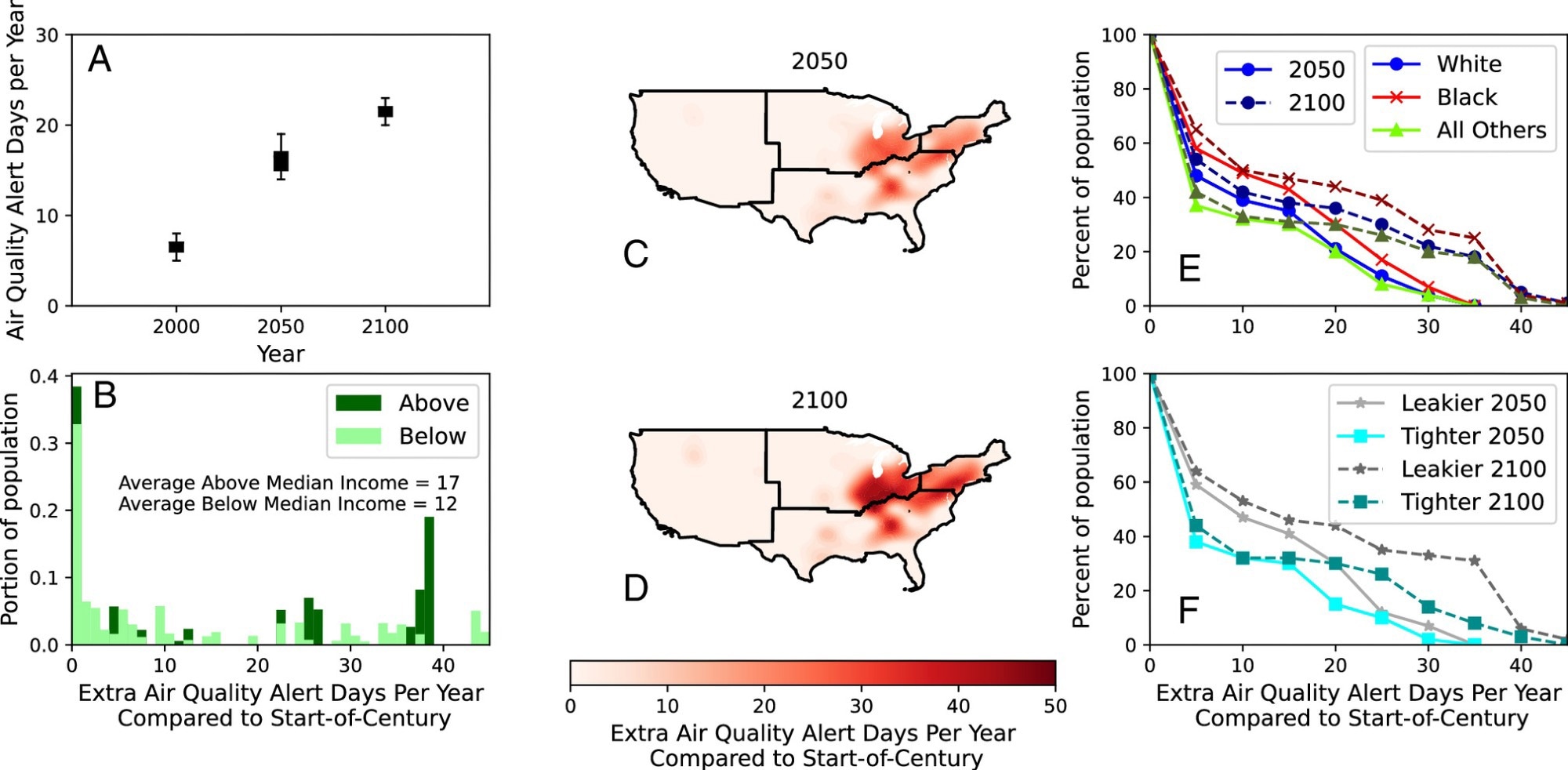 Air high quality alert days per 12 months (ADY) rise within the absence of emission reductions. All plots present air high quality alerts (outlined as outside high-quality particulate matter ranges leading to an Air High quality Index > 100) for the Reference (REF) local weather change situation. (A) Nationwide imply inhabitants weighted ADY for 2000, 2050, and 2100. Plots (B–F) present Additional ADY (EADY) in comparison with start-of-century (B) Histogram of EADY in 2100 for inhabitants above and under median earnings. (C/D) Spatial change in EADY in 2050 and 2100. (E) Cumulative density of EADY by race in 2050 and 2100. (F) Cumulative density of EADY by residential leakage charges above (“Leakier”) and under (“Tighter”) the nationwide common. Leakage is outlined as air adjustments per hour at a 50 Pa stress distinction (ACH50), indicating larger infiltration of out of doors air inside.
Air high quality alert days per 12 months (ADY) rise within the absence of emission reductions. All plots present air high quality alerts (outlined as outside high-quality particulate matter ranges leading to an Air High quality Index > 100) for the Reference (REF) local weather change situation. (A) Nationwide imply inhabitants weighted ADY for 2000, 2050, and 2100. Plots (B–F) present Additional ADY (EADY) in comparison with start-of-century (B) Histogram of EADY in 2100 for inhabitants above and under median earnings. (C/D) Spatial change in EADY in 2050 and 2100. (E) Cumulative density of EADY by race in 2050 and 2100. (F) Cumulative density of EADY by residential leakage charges above (“Leakier”) and under (“Tighter”) the nationwide common. Leakage is outlined as air adjustments per hour at a 50 Pa stress distinction (ACH50), indicating larger infiltration of out of doors air inside.
Adaptation to air air pollution versus mitigation of air air pollution
Antagonistic well being results and untimely mortality dangers related to air air pollution could be decreased by lowering publicity to polluted air (adaptation) or lowering the emission of greenhouse gases and air pollution (mitigation). These two methods have been in contrast on this research.
The findings revealed that adaptation gives extra advantages than mitigation. Nevertheless, an entire adaptation would require folks to remain at residence with home windows and doorways closed for an extra 142 days per 12 months, which may solely be achieved at a median value of 11,000 USD per individual. In distinction, lowering emissions can present important annual well being advantages at a median value of 5,400 USD per individual.
The findings additionally revealed that combining adaptation and mitigation can present the best complete advantages. The mixture of those methods might cut back the effectiveness of every technique when used alone.
Though the research evaluation indicated that mitigation is cheaper than adaptation, it stays extremely unsure to what extent mitigation of air air pollution is feasible and the way it will finally have an effect on outside air pollution. These uncertainties demand for an induction of particular person adaptation.
Concerning the advantages of adaptation, the research discovered a median good thing about 31 USD per individual per hour for adults aged 30 years and above. Thus, an applicable adaptation coverage and mitigation methods are wanted to successfully and equitably defend normal and weak populations from air air pollution.
Based on the research findings, adaptation could possibly be extra helpful for individuals who reside in polluted areas, work or reside in high-quality buildings, or don’t worth their outside time regardless of frequently spending time open air. Moreover, the research projected that individuals who by no means spend time open air, reside in poorly structured homes, or extremely worth their outside time wouldn’t profit from further adaptation.
Total, the research signifies that new insurance policies are wanted to extend adaptation charges and maximize safety from air air pollution. New insurance policies might compensate folks for transferring indoors, enhance home high quality, present measures for individuals who work or reside open air, and improve consciousness about air high quality alerts and adaptation methods.
Supply hyperlink








