In a current large-scale potential cohort examine revealed in JAMA Community Open, researchers evaluated whether or not increased dietary niacin consumption lowers the chance of all-cause, coronary heart and cerebrovascular illness(s)-related mortality in adults with non-alcoholic fatty liver illness (NAFLD) in the USA (US).
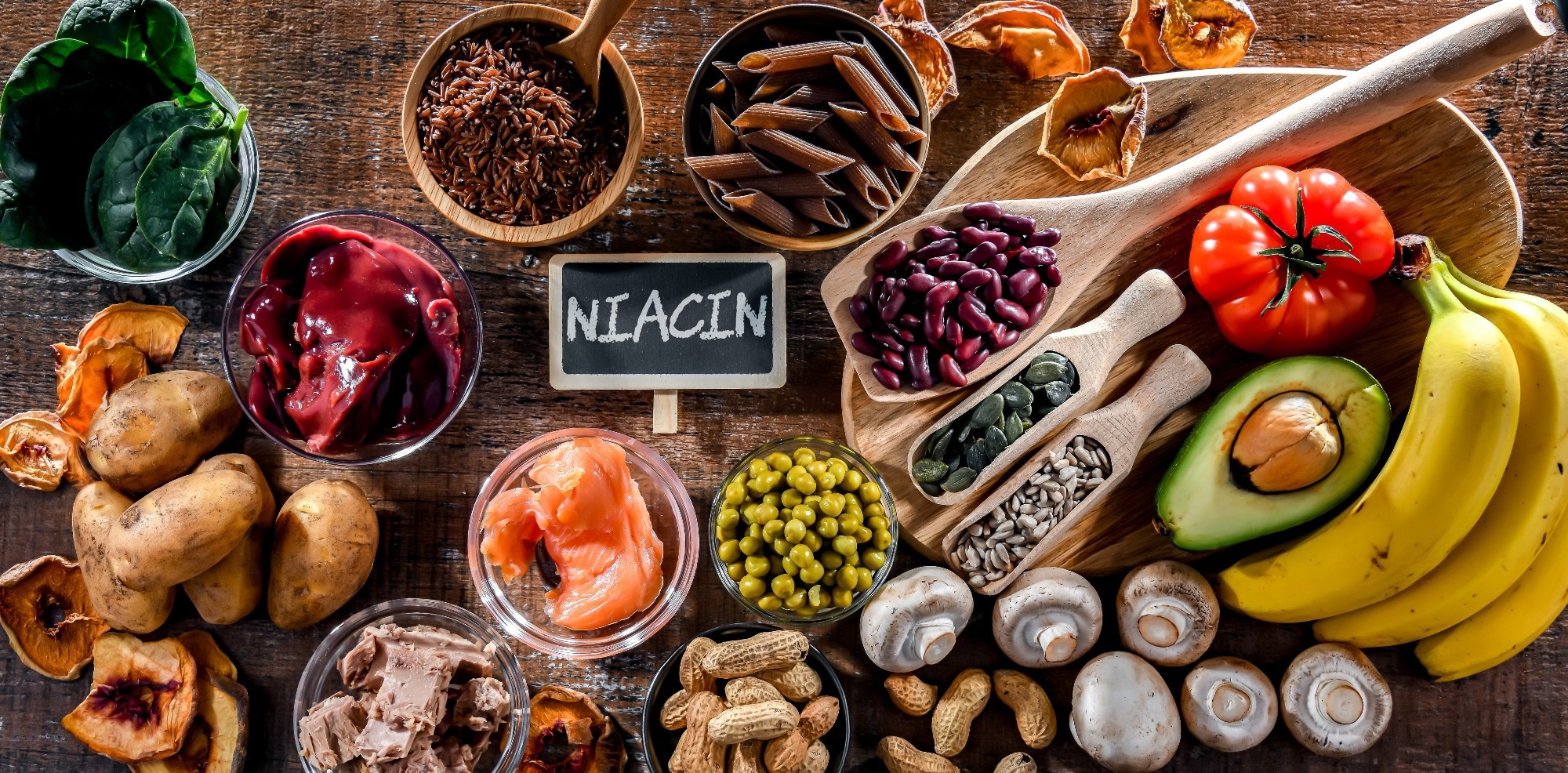 Examine: Dietary Niacin Consumption and Mortality Amongst People With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Illness. Picture Credit score: monticello/Shutterstock.com
Examine: Dietary Niacin Consumption and Mortality Amongst People With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Illness. Picture Credit score: monticello/Shutterstock.com
Background
The burden of NAFLD is surging worldwide, with the estimated prevalence of the illness reaching 32.4% globally and 47.8% within the US. Even the NAFLD mortality has doubled up to now three many years globally.
Present proof signifies that cardiovascular illnesses (CVDs) are the first reason behind demise amongst sufferers with NAFLD.
But, no potential research have assessed the affiliation between diet, particularly, niacin consumption and mortality danger in sufferers with NAFLD.
A earlier animal examine confirmed that niacin supplementation elevated nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) ranges to assist revive a fatty liver, and a examine with human topics confirmed the way it improved muscle efficiency.
Niacin, or vitamin B3, is a precursor of NAD and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP) synthesis, two pyridine coenzymes that play important roles in a number of metabolic, vitality metabolism, and redox reactions.
Preclinical research have additionally proven that niacin inhibits or reverses irritation and hepatic steatosis to stop fibrosis.
In regards to the examine
Within the current examine, researchers used information from US adults aged ≥20 who participated in eight cycles of the Nationwide Well being and Vitamin Examination Survey (NHANES) spanning 2003 to 2018.
They categorized all into three teams of people aged ≤39, 40-59, and ≥60.
They self-reported information on hypertension, dyslipidemia, and diabetes. Different examine covariates have been race/ethnicity, academic standing, revenue, physique mass index (BMI), use of dietary dietary supplements, bodily exercise, and smoking standing.
The crew ascertained mortality by linking the NHANES information to the Nationwide Dying Index information by December 31, 2019.
Likewise, they measured dietary niacin consumption utilizing a standardized Automated A number of-Move Technique (AMPM), which concerned two 24-hour dietary recall interviews, one performed in individual and the opposite over the phone, to gather information on the categories and meals portions consumed by every participant.
They calculated their day by day dietary niacin consumption primarily based on the common of the contributors’ two weight loss program remembers.
Statistical evaluation on this examine integrated unweighted frequencies and weighted percentages for categorical variables, whereas they used medians and IQRs for steady variables.
The researchers used the weighted Cox proportional hazards fashions to guage the relationships between dietary niacin consumption and all-cause and CVD mortalities, presenting outcomes as hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Moreover, they used restricted cubic spline evaluation to research the nonlinear associations between dietary niacin consumption and mortality, additional stratifying them to evaluate interactions with varied components.
Outcomes
All in all, 80,312 individuals participated in NHANES from 2003 to 2018, of whom 6,540 had a Fatty Liver Index (FLI) of ≥30; nevertheless, from these, solely 4,315 had confirmed NAFLD, and most have been males.
The baseline traits of the examine contributors diverse primarily based on dietary niacin consumption; for example, these with increased dietary niacin consumption have been youthful and sometimes male.
The authors famous an affiliation of upper dietary niacin consumption (≥26.7 mg/d) with a 30% decrease danger of all-cause and ~50% decrease danger of CVDs-related mortality amongst NAFLD sufferers.
The latter affiliation grew to become insignificant after adjustment for doubtlessly confounding variables apart from age and gender.
Furthermore, the proof of a nonlinear affiliation between dietary niacin consumption and these two sorts of mortalities was missing.
In subgroup analyses, the affiliation of upper niacin consumption with mortality danger was sturdy just for NAFLD sufferers with out diabetes in comparison with the reference group.
The subgroups with and with out diabetes had HRs of 0.82 and 0.58 for all-cause mortality in comparison with the reference group, respectively, P= 0.04 for interplay.
Within the subgroup of adults with vitamin B6 consumption <1.7 mg, the HR of all-cause mortality was 0.26, indicating they might profit extra from niacin consumption through weight loss program. Notably, vitamin B6 is important for the biosynthesis of niacin and its metabolism.
A day by day niacin dose of a minimal of 20 mg additionally meets the requirement for NAD+ synthesis, any dysregulation of which is related to CVD, weight problems, and neurodegenerative illnesses.
Stratified and sensitivity analyses additional demonstrated the robustness of those outcomes.
Conclusions
General, the outcomes of the current examine performed amongst NAFLD sufferers counsel an affiliation between increased dietary niacin consumption and decrease all-cause mortality.
Nonetheless, there was no inverse affiliation between dietary niacin consumption and the chance of CVD mortality.
Future research ought to examine the dose-response correlation of dietary niacin consumption with mortality to find out its optimum dosages for sufferers with NAFLD.
Supply hyperlink