In a latest examine printed within the journal Nature, researchers carried out cutting-edge genomic analysis on 2,000-year-old Brazilian human stays to research the evolution and emergence of ancestral treponemal genomes throughout the Americas and the Outdated World. They reconstruct 4 such historical genomes and discover that the prehistoric treponemal pathogen’s most carefully associated extant relative is Treponema pallidum endemicum, the pathogen chargeable for bejel. These findings problem the earlier hypotheses characterizing treponeme subspecies and spotlight that treponemes are rather more adaptable than hitherto thought.
 Research: Redefining the treponemal historical past by pre-Columbian genomes from Brazil. Picture Credit score: bekirevren / Shutterstock
Research: Redefining the treponemal historical past by pre-Columbian genomes from Brazil. Picture Credit score: bekirevren / Shutterstock
What are treponemes?
Treponemes are a genus of spiral-shaped micro organism, a few of that are chargeable for treponemal infections akin to syphilis Treponema pallidum pallidum [TPA]), bejel (T. pallidum endemicum [TEN]), and yaws (T. pallidum pertenue [TPE]). Whereas standard antibiotics have considerably decreased the burden of those pathogens, latest analysis is more and more discovering proof of treponemes creating multi-antibiotic resistance, inflicting a resurgence in medical and scientific research of those micro organism.
Regardless of various by solely 0.03% of their genome sequences, TPA, TEN, and TPE show remarkably totally different ecologies and pathologies. Bejel is discovered within the scorching, arid areas of western Asia and the japanese Mediterranean, yaws are restricted to the humid tropical components of Africa and South America, and syphilis is world. Medical data reveal that whereas syphilis is indiscriminative of its hosts’ regional improvement standing, bejel and yaws can solely be present in creating nations and have been eradicated from the developed world.
What will we find out about their historical past?
Syphilis and T. pallidum pallidum have acquired rather more tutorial curiosity than bejel and yaws regardless of all three ailments having comparable signs and medical interventions. That is in all probability as a result of former’s notoriety – syphilis was chargeable for a devastating European outbreak in 1495. Whereas Europe has been proposed as a possible origin for ancestral strains of treponemes, there stays a depth of literature testing this speculation, made harder by the diagnoses of historic infections that solely depart seen markings on 5-30% of superior instances.
Presently, two competing hypotheses exist for the presence of syphilis in Europe have been proposed – the pre-Columbian speculation and the Columbian speculation. The previous is supported by palaeopathological proof and postulates that the bacterium existed and possibly originated in Europe a whole bunch or 1000’s of years earlier than Columbus’ first American expedition. In distinction, the second postulates that it was Columbus and the colonists that adopted that carried treponemes to the continent.
The few research which have tried to unravel the genetics of treponemes have confirmed difficult, given the extreme lack of historical treponemal DNA. Understanding these pathogens’ evolutionary historical past and systematics would inform future research on optimum insurance policies to organize for potential illness outbreaks.
Concerning the examine
Within the current examine, researchers used practically 2,000-year-old human stays from the Jabuticabeira II burial web site to reconstruct 4 ancestral T. pallidum genomes with as much as 33.6× protection. The pattern group comprised 96 specimens from the burial web site, each with (n = 32) and with out suspected treponemal pathologies. Preliminary screening revealed 37 specimens with usable treponemal DNA.
All samples have been radiocarbon-dated, with 4 bone samples yielding the mandatory genomic DNA. Shotgun sequencing was used for preliminary pathogen screening. Goal enrichment of sequenced DNA revealed 9 samples with greater than 5,000 reads mapping to T. pallidum reference genomes (acquired from BosniaA, CDC2, and Nichols). The 4 aforementioned bone samples (ZH1390, ZH1540, ZH1541, and ZH1557) have been discovered to have reads overlaying 9.2-99.4% of the BosniaA reference genome.
Base deamination was estimated to confirm the authenticity of recovered historical DNA. Excessive-throughput Illumina sequencing of ZH1390, ZH1540, ZH1541, and ZH1557 was used to generate reads for ancestral genome reconstruction. These reads have been subsequently mapped to reference TPE (CDC2), TEN (BosniaA), and TPA (Nichols) genomes.
“The ultimate sequence obtained for the ZH1540 pattern resulted in 99.38% protection with respect to the TEN reference genome (BosniaA), a minimal protection depth of 5× and a median depth of 33.6×.”
The newly generated ZH1540 historical genome was assembled (aligned) and analyzed along with 98 treponeme genomes, together with TEN (8 strains), TPE (30 strains), and TPA (60 strains), all acquired from the Nationwide Middle for Biotechnology Info (NCBI) and European Nucleotide Archive (ENA) databases. The ensuing alignment spanned 1,141,812 nucleotides and included 6149 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).
Inheritance patterns and phylogenetic analyses have been carried out utilizing a recombination evaluation with the phylogenetic incongruence technique (PIM). Relatedness was visualized utilizing Most-likelihood tree-building approaches. To find out the age of the reconstructed genome, molecular clock relationship was carried out.
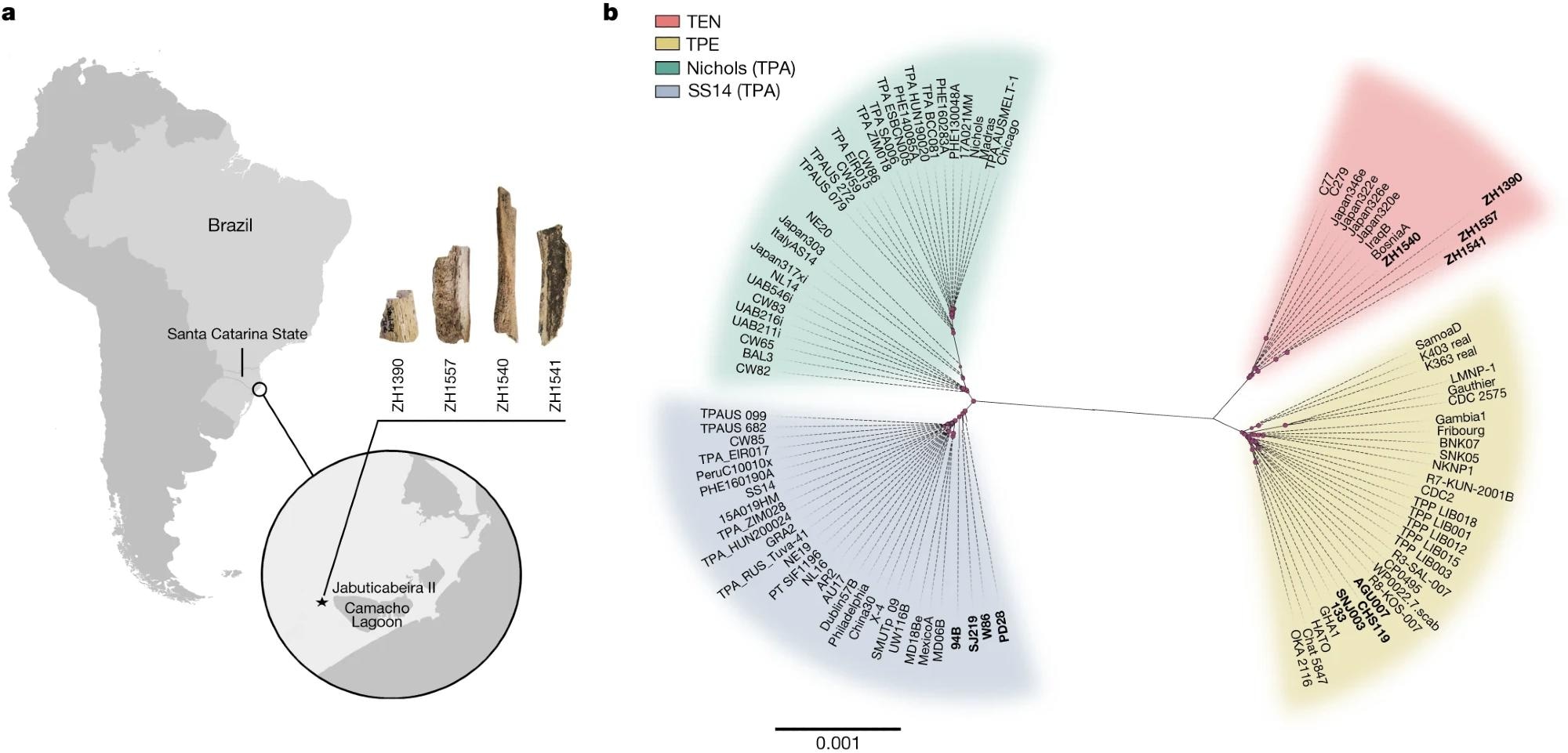 a, A map exhibiting the placement of the Jabuticabeira II archaeological web site on the south coast of Santa Catarina state, Brazil, and the samples ZH1390, ZH1540, ZH1541 and ZH1557, for which genomes have been reconstructed. b, A maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of the fashionable and historical T. pallidum strains utilizing GTR + G + I because the evolutionary mannequin and 1,000 bootstrap repetitions. All historical genomes utilized in this examine (newly reconstructed and beforehand printed historical genomes; see Supplementary Desk 3) are marked in daring. Pink dots symbolize nodes with bootstrap values exceeding 70%. The dimensions bar is in models per substitutions per web site.
a, A map exhibiting the placement of the Jabuticabeira II archaeological web site on the south coast of Santa Catarina state, Brazil, and the samples ZH1390, ZH1540, ZH1541 and ZH1557, for which genomes have been reconstructed. b, A maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of the fashionable and historical T. pallidum strains utilizing GTR + G + I because the evolutionary mannequin and 1,000 bootstrap repetitions. All historical genomes utilized in this examine (newly reconstructed and beforehand printed historical genomes; see Supplementary Desk 3) are marked in daring. Pink dots symbolize nodes with bootstrap values exceeding 70%. The dimensions bar is in models per substitutions per web site.
Research findings
The current examine generated 4 historical treponeme genomes, all of which have been unexpectedly most carefully associated to the bejel-causing T. pallidum endemicum. Whereas syphilis and yaws have been recognized from Outdated and New World historical genomes, these symbolize the primary TEN-like pathogens ever remoted from archaeological stays.
“Our findings on this examine solely implement this view: an historical, TEN-like agent, recognized removed from the illness’s modern-day geographical area of interest, in a damp Brazilian coastal area attests to the power of treponemes to adapt to numerous climates and geographic areas. Excessive-quality treponemal DNA recovered from a prehistoric supply validates the usage of historical DNA methods in establishing a completely novel, extra knowledgeable speculation on the occasions resulting in the unfold of Treponema pallidum the world over.”
Molecular clock analyses reveal that the T. pallidum cohort is far older than beforehand believed, by greater than 1,000 years. The cohort can be seen as being extremely adaptable, suggesting that its ancestral vary far exceeds in the present day’s.
“Lastly, because the breakthrough discovery of a pre-Columbian treponematosis right here is the results of a mixture of historical pathogen genomics and the cautious number of archaeological samples, we are able to count on future findings to light up the occasions resulting in the rise and unfold of venereal syphilis, and assist resolve the evolutionary components chargeable for the worldwide success of the Treponema household.”
Journal reference:
- Majander, Okay., Du Plessis, L., Arora, N., Filippini, J., Eggers, S., & Schuenemann, V. J. (2024). Redefining the treponemal historical past by pre-Columbian genomes from Brazil. Nature, 1-7, DOI – 10.1038/s41586-023-06965-x, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06965-x
Supply hyperlink








